
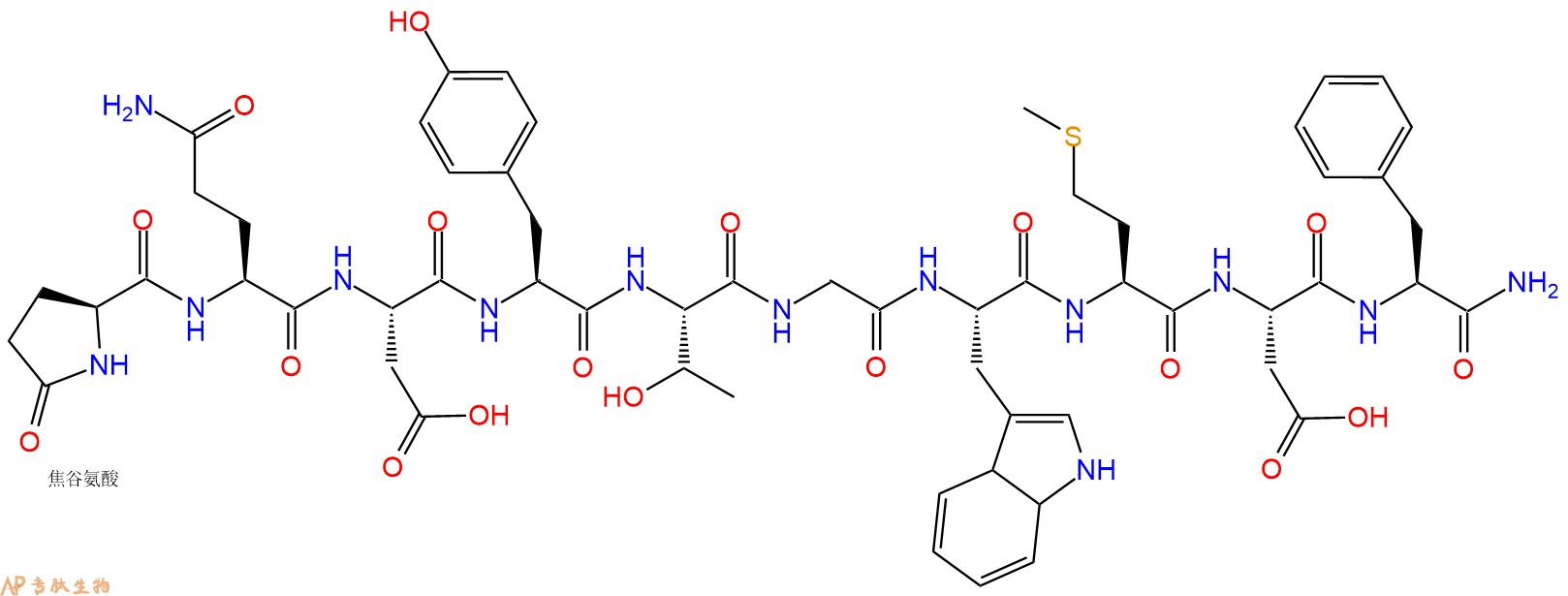
pygmaeus.ĪB - Peptidomic analysis of norepinephrine-stimulated skin secretions of the tetraploid frog Xenopus fraseri Boulenger, 1905 (Pipidae) led to identification of 13 host-defense peptides. andrei but suggest a more distant relationship with X. Cladistic analyses based upon the primary structures of magainin, PGLa, and CPF-RP peptides support a close evolutionary relationship between X. fraseri has been placed in a species group that includes the octoploids Xenopus amieti and Xenopus andrei, and the tetraploid Xenopus pygmaeus. On the basis of similarities in morphology and advertisement calls, X. The most potent antimicrobial peptide identified is CPF-RP-F1 (GFGSVLGKALKFGANLL.NH2) with MIC = 12.5 μM against Staphylococcus aureus and 50 μM against Escherichia coli. laevis xenopsin and peptide glycine-tyrosine-amide (PGYa) (GRIIPIYPEFERVFA KKVYPLY.NH2) whose function is unknown. In addition, the secretions contain a molecular variant of xenopsin displaying the substitution Arg4 → Lys compared with X.
The primary structures of the peptides demonstrate that they belong to the magainin (3 peptides), peptide glycine-leucine-amide, PGLa (4 peptides), and xenopsin-precursor fragment, XPF (2 peptides) families, first identified in Xenopus laevis, together with caerulein precursor fragment-related peptides, CPF-RP (4 peptides), first identified in Silurana tropicalis. N2 - Peptidomic analysis of norepinephrine-stimulated skin secretions of the tetraploid frog Xenopus fraseri Boulenger, 1905 (Pipidae) led to identification of 13 host-defense peptides. T2 - Further insight into the evolutionary history of the Xenopodinae T1 - Host-defense peptides from skin secretions of Fraser's clawed frog Xenopus fraseri (Pipidae) pygmaeus.Ībstract = "Peptidomic analysis of norepinephrine-stimulated skin secretions of the tetraploid frog Xenopus fraseri Boulenger, 1905 (Pipidae) led to identification of 13 host-defense peptides.

The most potent antimicrobial peptide identified is CPF-RP-F1 (GFGSVLGKALKFGANLL.NH 2) with MIC = 12.5 μM against Staphylococcus aureus and 50 μM against Escherichia coli. laevis xenopsin and peptide glycine-tyrosine-amide (PGYa) (GRIIPIYPEFERVFA KKVYPLY.NH 2) whose function is unknown. In addition, the secretions contain a molecular variant of xenopsin displaying the substitution Arg 4 → Lys compared with X. Peptidomic analysis of norepinephrine-stimulated skin secretions of the tetraploid frog Xenopus fraseri Boulenger, 1905 (Pipidae) led to identification of 13 host-defense peptides.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
